Process Creation, System calls related to the process, cooperation between processes , Message Passing, Interprocess communication
fork() system call
A process is created by the fork() system call.
- created a new address space that is a duplicate of the caller
int main(){
int pid;
pid = fork();
if(pid == 0){ /* this is child */ Child process -> pid = 0
printf("\n Hello, I am child!\n");
}else if(pid>0) { /*this is parent */
printf("\n Hello, I am parent!\n"); Parent process -> pid > 0
}
}exec() system call
A process can execute a diffent program by the exec() system call.
- replaces the memory image of the caller with a new program.
int main(){
int pid;
pid = fork();
if(pid == 0){ /* this is child */ Child process -> pid = 0
printf("\n Hello, I am child! Now i'll run date \n");
execlp("/bin/date", "/bin/date",(char)0);
}else if(pid>0) { /*this is parent */
printf("\n Hello, I am parent!\n"); Parent process -> pid > 0
}
}wait() system call
when process 'A' calls wait() system call
- The Kernel puts process A to sleep until the child terminates. (block state)
- once the child process terminates, the kernel wakes up process A (ready state)
int main(){
int childPid;
s;
childPid = fork();
if(pid == 0){ /* this is child */ Child process -> pid = 0
<code for child process>
}else{
wait();
}
s;
}exit() system call
Terminates of process
- Voluntary termination
- Through exit() system call after the last statement was performed.
- The compiler automatically inserts it at the end of the 'main' function, even if not explicitly specified in the program
- Non-Voluntary termination
- The parent process forcefully terminates the child process
- If the child process requests the resources beyond the maximum limit.
- the task assigned to the child is no longer required.
- When the type 'kill', 'break' or similar commands on the keyboard.
- When it is terminated by the parent
- The children terminates before the parent process.
- The parent process forcefully terminates the child process
Colaboration between processes
Independent process
- Each process has its own address space so, in principle, one process can't affect the execution of another process
Cooperating process
- Through IPC , one process can affect the execution of another process
IPC(Interprocess Communication)
- The method of message passing.
- message passing : message passing through the kernel
- The method of sharing the address space
- shared memory : There is shared memory mechanism that allows certain parts of the address space to be shared even among different processes.
- Thread : thread는 사실상 하나의 프로세스이므로 프로세스 간 협력으로 보기는 어렵지만 동일한 process를 구성하는 thread들 간에는 주소 공간을 공유하므로 협력이 가능

Message Passing
Message system
- 프로세스 사이에 공유 변수(shared variable)를 일체 사용하지 않고 통신하는 시스템
Direct Communication
- 통신하려는 프로세스의 이름을 명시적으로 표시
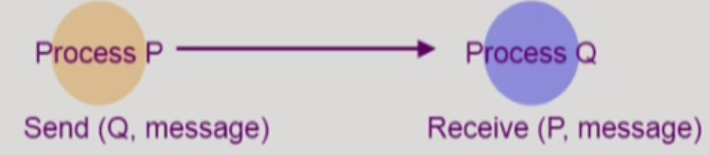
Indirect Communication
- mailbox(또는 port)를 통해 메시지를 간접 전달

'OS(운영체제)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Scheduling Algorithm(FCFS,SJF,Priority,RR, Multilevel, etc.) (0) | 2023.08.06 |
|---|---|
| CPU Scheduling 1 (0) | 2023.07.29 |
| Process Management 1 (0) | 2023.07.29 |
| Process 2~3 (0) | 2023.07.29 |
| Process 1 (0) | 2023.07.29 |


